Rigid packaging stands as one of the most premium and durable packaging solutions in modern product manufacturing. With its sturdiness, structural integrity, and luxurious appearance, rigid packaging has become the preferred choice for high-end brands seeking to create memorable unboxing experiences and deliver exceptional product protection.
But how does rigid packaging differ from the other two major packaging categories—folding cartons and corrugated boxes? When should businesses opt for one over the other?
This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown:
• Definition of rigid packaging
• Material composition
• Manufacturing processes
• Application scenarios
• Key advantages
• Limitations
• Detailed comparison with folding cartons and corrugated boxes
Whether you are a brand owner, product developer, procurement specialist, or packaging designer, this guide will help you understand rigid packaging’s position in today’s market and master the essentials for selecting the optimal packaging solution for your products.
What Is Rigid Packaging?
Rigid packaging refers to containers made from thick, sturdy cardboard that resists folding, bending, or collapsing. Typically 4-5 times thicker than standard folding carton material, it offers exceptional durability and a premium tactile feel. It does not bend or collapse under pressure. It maintains its shape from production through delivery, remaining stable during transport, storage, and on retail shelves.
Its structure is typically formed through:
– Solid corrugated cardboard or grayboard core
– Wrapped in printed specialty paper
– Surface coated with varnish, laminate, foil, or composite materials
Unlike foldable cartons that flatten for shipping, rigid packaging cannot be transported flat and possesses a permanent shape.
Core Characteristics of Rigid Packaging
· High structural strength
· Luxurious visual and tactile appeal
· Suitable for luxury goods or fragile items
· Supports diverse customization
· Resistant to collapse and folding
Rigid packaging boxes are widely used in jewelry, cosmetics, electronics, gift packaging, premium beverages, and promotional items.
2. Common Types of Rigid Packaging
Rigid packaging can take many structural forms. Below are the most commonly used types:
2.1 Rigid Setup Box (Two-Piece Box)
Often used for luxury items:
Top lid + bottom base
Strong structure
Ideal for electronics, premium cosmetics, and gift sets

2.2 Magnetic Closure Rigid Boxes
Features an elegant magnetic flap that snaps into place:
Popular for tech accessories, influencer kits, and premium brands
Excellent for unboxing experiences

2.3 Drawer / Slide Rigid Boxes
Sleeve + inner tray design:
Creates a high-end reveal
Often used in jewelry, fragrance, and stationery

2.4 Round / Cylindrical Rigid Boxes
Made from rolled rigid board:
Used for candles, foods, teas, fashion accessories

Rigid packaging is highly customizable in shape, opening style, inserts, and overall design.
3. Materials Used in Rigid Packaging
Rigid packaging uses stronger materials compared to folding cartons.
3.1 Greyboard / Chipboard
The core material for most rigid boxes
Thickness ranges from 1mm to 3mm
Provides structural strength
3.2 Wrapped Paper
The outer covering that provides aesthetics:
Art paper
Kraft paper
Textured specialty paper
Fabric or leatherette paper
Foil paper
3.3 Inserts
To secure products inside:
EVA foam
Paperboard insert
Foam board
Molded pulp
Because the board is thick and wrapped, rigid packaging offers both protection and aesthetic versatility.
4. Advantages of Rigid Packaging
Rigid packaging provides brand and product benefits not achievable with other packaging types.
4.1 Premium Branding and Shelf Appeal
The strong structure and wrapped finishes create a luxury feel that elevates product value.
4.2 High Structural Strength
Protects delicate, fragile, and expensive items.
4.3 Exceptional Customization Options
Supports:
Embossing & debossing
Foil stamping
Spot UV
Laminations (matte, gloss, soft-touch)
Window cutouts
Magnetic closures
Specialty textures
4.4 Excellent for Unboxing Experiences
Influencer and social media marketing favor rigid boxes for their premium reveal.
4.5 Long-Term Reusability
Many consumers repurpose rigid boxes for storage, extending brand visibility.
5. Limitations of Rigid Packaging
Despite its many strengths, rigid packaging has restrictions.
5.1 Higher Cost
Rigid boxes cost more due to:
Thick board
Hand-assembly
Additional wrapping and finishing processes
5.2 Higher Shipping Costs
Because rigid boxes cannot “collapse flat,” they occupy more space during transport.
5.3 Longer Production Time
Many rigid boxes require manual labor, extending lead time.
5.4 Less Eco-friendly When Over-laminated
Some finishing methods reduce recyclability unless eco-friendly options are chosen.
6. What Are Folding Cartons?
Now let’s compare rigid packaging with folding cartons.
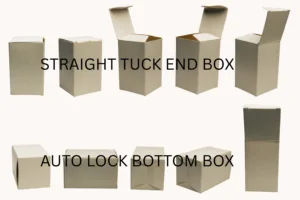
Folding cartons are packaging made from thinner paperboard (usually 250–400gsm) that can be folded flat.
Examples include:
Tuck-end boxes
Snap-lock bottom boxes
Hang tab boxes
Display cartons
Benefits of Folding Cartons
Lower cost
Lightweight
Ships flat, saving logistics cost
Easy to print and customize
Limitations
Less durable
Not suitable for luxury positioning
Cannot carry heavy products without reinforcement
7. What Are Corrugated Boxes?
Corrugated boxes are made from fluted corrugated board, consisting of:
An outer liner
A fluted layer
An inner liner
They offer excellent strength for shipping and heavy goods.
Benefits of Corrugated Boxes
Maximum strength and protection
Ideal for e-commerce and logistics
Cost-effective
Fully recyclable
Limitations
Not as visually premium as rigid packaging
Bulkier than folding cartons
8. Rigid Packaging vs. Folding Cartons vs. Corrugated Boxes
Below is a detailed comparison to help businesses choose the right packaging solution.
8.1 Structural Strength
| Packaging Type | Strength Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid Packaging | ★★★★☆ | Strong and durable, does not collapse |
| Folding Cartons | ★★☆☆☆ | Lightweight, less resistant to impact |
| Corrugated Boxes | ★★★★★ | Best option for protection and shipping |
Rigid is strong, corrugated is the strongest.
8.2 Visual Appeal
| Packaging Type | Visual Quality | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid Packaging | ★★★★★ | Most luxurious and premium |
| Folding Cartons | ★★★☆☆ | Clean, printable, but less premium |
| Corrugated Boxes | ★★☆☆☆ | Usually plain unless printed |
Rigid boxes are ideal for luxury branding.
8.3 Customization Options
| Packaging Type | Customization | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid | Highest | Options include magnetic closures, wrapped textures, complex shapes |
| Folding Carton | Medium | Simple box structures, printing, coatings |
| Corrugated | Low–Medium | Mostly structural customization, limited luxury finishes |
Rigid boxes allow the most sophisticated upgrades.
8.4 Cost Comparison
| Packaging Type | Cost Level |
|---|---|
| Rigid Packaging | High |
| Folding Cartons | Low |
| Corrugated Boxes | Medium |
Rigid packaging is the most expensive due to materials and labor.
8.5 Shipping & Storage Efficiency
| Packaging Type | Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Rigid Packaging | Low (non-collapsible) |
| Folding Cartons | Excellent (ships flat) |
| Corrugated Boxes | Good |
Folding cartons offer the greatest logistics savings.
8.6 Best Use Cases
Rigid Packaging
Luxury products
Cosmetics & skincare
Jewelry
Electronics
Premium gifts
Brand experience boxes
Folding Cartons
Lightweight retail products
Food, beauty, supplements
Point-of-sale displays
Inner packaging
Corrugated Boxes
Shipping
E-commerce
Heavy goods
Protective secondary packaging
9. Packaging Trends in 2025: Where Rigid Packaging Stands
Rigid packaging continues to evolve. Key trends include:
9.1 Sustainable Rigid Packaging
Recycled greyboard
FSC-certified wrap papers
Plastic-free inserts
Water-based inks
9.2 Premium Unboxing for E-commerce
Brands invest heavily in:
Magnetic boxes
Drawer boxes
Personalized inserts
9.3 Hybrid Packaging
Rigid outer shell + corrugated inner support for fragile products.
9.4 Minimalist & Soft-Touch Design
Matte soft-touch laminations and simple typography dominate luxury branding.
9.5 Automation in Rigid Box Production
More suppliers adopt semi-automatic equipment to reduce cost and lead times.
Rigid packaging remains the standard for premium positioning.
10. How to Choose the Right Packaging for Your Product
To make the right decision, consider:
10.1 Product Weight & Fragility
Heavy or fragile → corrugated or rigid
Lightweight → folding carton
10.2 Brand Positioning
Luxury & gifting → rigid
Mainstream retail → folding carton
10.3 Budget
Tight budget → folding carton or corrugated
High-value item → rigid
10.4 Logistics Requirements
Need flat shipping → folding carton
Accept full-size shipping → rigid
10.5 Consumer Experience
Want a “wow” unboxing → rigid packaging
11. Conclusion
Rigid packaging plays a crucial role in shaping premium brand identity and protecting high-value products. Its durability, sophisticated finishes, and luxurious feel set it apart from folding cartons and corrugated boxes.
If you need luxury, structure, and a memorable unboxing, choose rigid packaging.
If you need cost efficiency and versatility, choose folding cartons.
If you need maximum strength for transport, choose corrugated boxes.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each packaging type allows brands to make strategic decisions that balance cost, performance, and aesthetics. In today’s competitive marketplace, choosing the right packaging is not just a logistics decision—it is a branding strategy that shapes customer perception and long-term loyalty.
Partner with Bonroy and build your rigid packaging business!